ᵃ ʷⁱˢᵉ ᵐᵃⁿ ⁿᵉᵛᵉʳ ᶠᵃˡˡ ⁱⁿ ˡᵒᵛᵉ
前言
本文主要介绍:
- Cron 表达式
- java中调度框架的实现何使用
- ooize调度框架的使用
“编程中常使用的调度任务”
定时任务 -> 调度框架
1. cron表达式
1.1 Cron表达式的7个部分
(* * * * * * *)从左到右代表的含义如下:
Seconds Minutes Hours Day-of-Month Month Day-of-Week Year(可选填)
1.2 Cron表达式可选的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
字段名 允许的值 允许的特殊字符
秒 0-59 , - * /
分 0-59 , - * /
小时 0-23 , - * /
日 1-31 , - * ? / L W C
月 1-12 or JAN-DEC , - * /
周几 1-7 or SUN-SAT , - * ? / L C #
年 (可选字段) empty, 1970-2099 , - * /
1.3 Cron中的符号:
- ***** :
代表整个时间段. - / :
表示每多长时间执行一次 - **0/15 **:
表示每隔15分钟执行一次,“0”表示为从“0”分开始; - **3/20 **:
表示每隔20分钟执行一次,“3”表示从第3分钟开始执行 - ? :
表示每月的某一天,或第几周的某一天 - L :
“6L”表示“每月的最后一个星期五” - W:
如“15W”放在每月(day-of-month)字段上表示为“到本月15日最近的工作日” - #:
"6#3"或者"FRI#3":在每周(day-of-week)中表示“每月第三个星期五”
1.4 Linux/ooize 舍弃了秒的存在,从分钟开始
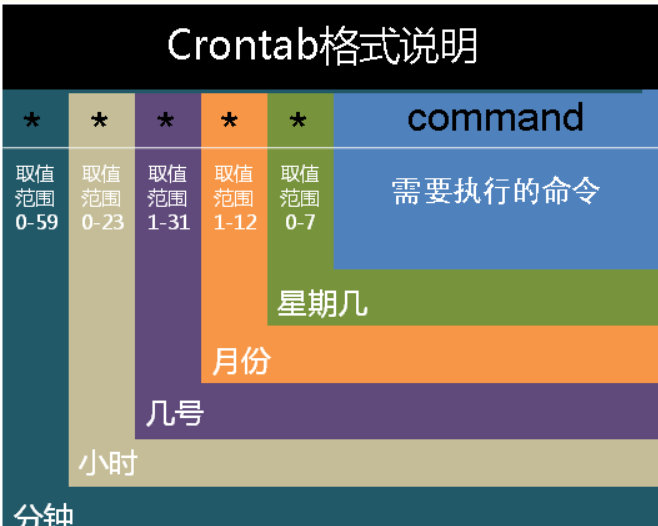
1.5 Cron eg:
- 0 0 12 ? * WED(每星期三下午12:00 执行)
- 1 * * * * *(每分钟1s时执行)
- 0 0 0-17,20-23 * * *(每天下午00:00 到17:00 执行,20:00 到23:00 执行)0 */5 * * * *(每5分种执行一次)
- Linux Crontab 定时任务
2. java定时任务
2.1 同步定时任务
2.1.1 Thread Sleep?
使用线程睡眠的方式每30s执行一次: 同步,等待时间 = 资源执行时间+30s :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
doSomeThings();
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
异步,等待时间 = 30s
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
while (true) {
new Thread(() -> {
doSomeThings();
});
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
明显这种方式比较笨拙,可优化点:
- new Thread()很笨拙,考虑使用线程池
- sleep不适用时间调度,考虑使用钩子函数(装饰者模式)
- 不支持cron调度
- 违反开闭原则(ocp),使用带设计模式的框架显然更好
2.2 异步单线程定时任务
2.2.1 Timer
简单使用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello!!!");
}
};
Timer timer = new Timer();
long delay = 0;
long intevalPeriod = 1 * 1000;
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(task, delay, intevalPeriod);
timer.schedule(task, delay);
内部实现:Timer实现分析
1.每一个任务执行前会先维护好下次任务将要执行的时间 2.如果queue中为空,那证明mainLoop(Boss)为空,wait了,就notified -> Boss
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
/**
* Schedule the specified timer task for execution at the specified
* time with the specified period, in milliseconds. If period is
* positive, the task is scheduled for repeated execution; if period is
* zero, the task is scheduled for one-time execution. Time is specified
* in Date.getTime() format. This method checks timer state, task state,
* and initial execution time, but not period.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if <tt>time</tt> is negative.
* @throws IllegalStateException if task was already scheduled or
* cancelled, timer was cancelled, or timer thread terminated.
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code task} is null
*/
private void sched(TimerTask task, long time, long period) {
if (time < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal execution time.");
// Constrain value of period sufficiently to prevent numeric
// overflow while still being effectively infinitely large.
if (Math.abs(period) > (Long.MAX_VALUE >> 1))
period >>= 1;
synchronized(queue) {
if (!thread.newTasksMayBeScheduled)
throw new IllegalStateException("Timer already cancelled.");
synchronized(task.lock) {
if (task.state != TimerTask.VIRGIN)
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Task already scheduled or cancelled");
task.nextExecutionTime = time;
task.period = period;
task.state = TimerTask.SCHEDULED;
}
queue.add(task);
if (queue.getMin() == task)
queue.notify();
}
}
- Boss线程去轮询待执行任务比较判断时间并run task
- 如果线程为空,防止while(true) 不停转,就把该线程wait了 : queue.wait(executionTime - currentTime);
- 等待超时时间过后,执行task的run方法
- wait够了就: task.run();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
/**
* The main timer loop. (See class comment.)
*/
private void mainLoop() {
while (true) {
try {
TimerTask task;
boolean taskFired;
synchronized(queue) {
// Wait for queue to become non-empty
while (queue.isEmpty() && newTasksMayBeScheduled)
queue.wait();
if (queue.isEmpty())
break; // Queue is empty and will forever remain; die
// Queue nonempty; look at first evt and do the right thing
long currentTime, executionTime;
task = queue.getMin();
synchronized(task.lock) {
if (task.state == TimerTask.CANCELLED) {
queue.removeMin();
continue; // No action required, poll queue again
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime = task.nextExecutionTime;
if (taskFired = (executionTime<=currentTime)) {
if (task.period == 0) { // Non-repeating, remove
queue.removeMin();
task.state = TimerTask.EXECUTED;
} else { // Repeating task, reschedule
queue.rescheduleMin(
task.period<0 ? currentTime - task.period
: executionTime + task.period);
}
}
}
if (!taskFired) // Task hasn't yet fired; wait
queue.wait(executionTime - currentTime);
}
if (taskFired) // Task fired; run it, holding no locks
task.run();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
2.3 多线程任务调度器
2.3.1 ScheduledExecutorService
优点:
- 异步 + 线程池调用,不受上个未执行完task影响(也可设定受影响)
简单使用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// task to run goes here
System.out.println("Hello !!");
}
};
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors
.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
// 第二个参数为首次执行的延时时间,第三个参数为定时执行的间隔时间
service.scheduleAtFixedRate(runnable, 10, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的 ScheduledFuture。
// 参数:
// callable - 要执行的功能
// delay - 从现在开始延迟执行的时间
// unit - 延迟参数的时间单位
// 返回:
// 可用于提取结果或取消的 ScheduledFuture
service.schedule(runnable, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
2.3.1三种方法:
- schedule的两个方法,延时delay时间后执行任务。区别Callable参数可以获取任务完成的结果值,Runnable参数的不会得到结果值。
- scheduleAtFixedRate方法:在延时initialDelay时间之后,开始第一次执行任务,然后每隔周期时间period,再次执行任务。注意如果任务消耗时间大于周期时间period,会等待任务完成之后,才再次执行任务。
- scheduleWithFixedDelay方法:在延时initialDelay时间之后,开始第一次执行任务,任务执行完成之后,再延时delay时间,然后再次执行任务。
3.2 Quartz框架
3.2.1 简单使用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class HelloJob implements Job{
public void execute(JobExecutionContext jobExecutionContext) throws JobExecutionException {
//打印当前的执行时间 例如 2017-11-23 00:00:00
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("现在的时间是:"+ sf.format(date));
//具体的业务逻辑
System.out.println("Hello Quartz");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws SchedulerException {
//创建一个jobDetail的实例,将该实例与HelloJob Class绑定
JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(HelloJob.class).withIdentity("myJob").build();
//创建一个Trigger触发器的实例,定义该job立即执行,并且每2秒执行一次,一直执行
SimpleTrigger trigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger().withIdentity("myTrigger").startNow().withSchedule(SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule().withIntervalInSeconds(2).repeatForever()).build();
//创建schedule实例
StdSchedulerFactory factory = new StdSchedulerFactory();
Scheduler scheduler = factory.getScheduler();
scheduler.start();
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail,trigger);
}
SimpleTrigger
简单的定时任务,可以采用SimpleTrigger
CronTrigger
可以设定单的触发时间表,更可以设定非常复杂的触发时间表。 CronTrigger 是基于 Unix类似于 cron 表达式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public static void main(String[] args) throws SchedulerException, InterruptedException {
//jobDetail
JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(HelloJob.class).withIdentity("cronJob").build();
//cronTrigger
//每日的9点40触发任务
CronTrigger cronTrigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger().withIdentity("cronTrigger").withSchedule(CronScheduleBuilder.cronSchedule("0 40 9 * * ? ")).build();
//1.每日10点15分触发 0 15 10 ?* *
//2.每天下午的2点到2点59分(正点开始,隔5分触发) 0 0/5 14 * * ?
//3.从周一到周五每天的上午10点15触发 0 15 10 ? MON-FRI
//4.每月的第三周的星期五上午10点15触发 0 15 10 ? * 6#3
//5.2016到2017年每月最后一周的星期五的10点15分触发 0 15 10 ? * 6L 2016-2017
//Scheduler实例
StdSchedulerFactory stdSchedulerFactory = new StdSchedulerFactory();
Scheduler scheduler = stdSchedulerFactory.getScheduler();
scheduler.start();
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail,cronTrigger);
}
3. 集群调度任务ooize
详情见我的: ooize使用到精通